ISHLT Consensus Statement on Short Telomere Syndrome and Lung Transplantation
Published 8 January 2026
Andrew Courtwright, MD, PhD; John Mackintosh; Jonathan Alder, PhD; Christine Kim Garcia, MD, PhD; Antoine Froidure, MD, PhD; Erin Lowery, MD, MS; Don Hayes, Jr., MD, MS, MEd, MBA; Pali Shah, MD; Quentin Philippot; Raphael Borie, MD, PhD; John Greenland, MD, PhD; Hannah Mannem, MD; Mark Snyder, MD; Merel Hellemons, MD, PhD; Laurie Snyder, MD, MHS; John McDyer, MD
J Heart Lung Transplant. January 2026.
NEW JHLT: The Podcast Episode
Featuring a discussion of the consensus statemetn findings and takeaways.
Motivated by growing evidence that the presence of critically shortened telomeres influences interstitial lung disease (ILD) trajectories, and is associated with extrapulmonary conditions relevant to transplant candidacy and post-transplant complications, this document is the result of work by an international writing committee with expertise in STS and is grounded in current literature and expert consensus.
This consensus document aims to address gaps in the evaluation and management of patients with STS, the need for this which arises from the recognition that STS is an underdiagnosed contributor to ILD, and that its presence introduces complexities that require dedicated, multidisciplinary attention in the transplant setting. Authors have included recommendations for screening, diagnosis, transplant risk stratification, peri- and post-transplant care, and research priorities in areas where substantial data are lacking.
JHLT: The Podcast
This constnsus statement is covered in Episode 77 of JHLT: The Podcast.
JHLT Digital Media Editors are joined by project leads Andrew Courtwright, MD, PhD, John Mackintosh, and John McDyer, MD to discuss the new document from ISHLT.
The conversation includes discussion of:
- Recommendations for assessing patients for STS
- Which patients we should screen
- How the diagnosis influences transplant decision making and risk assessment
- How STS impacts immunosuppression
- Extrapulmonary comorbidities
- Future areas for research
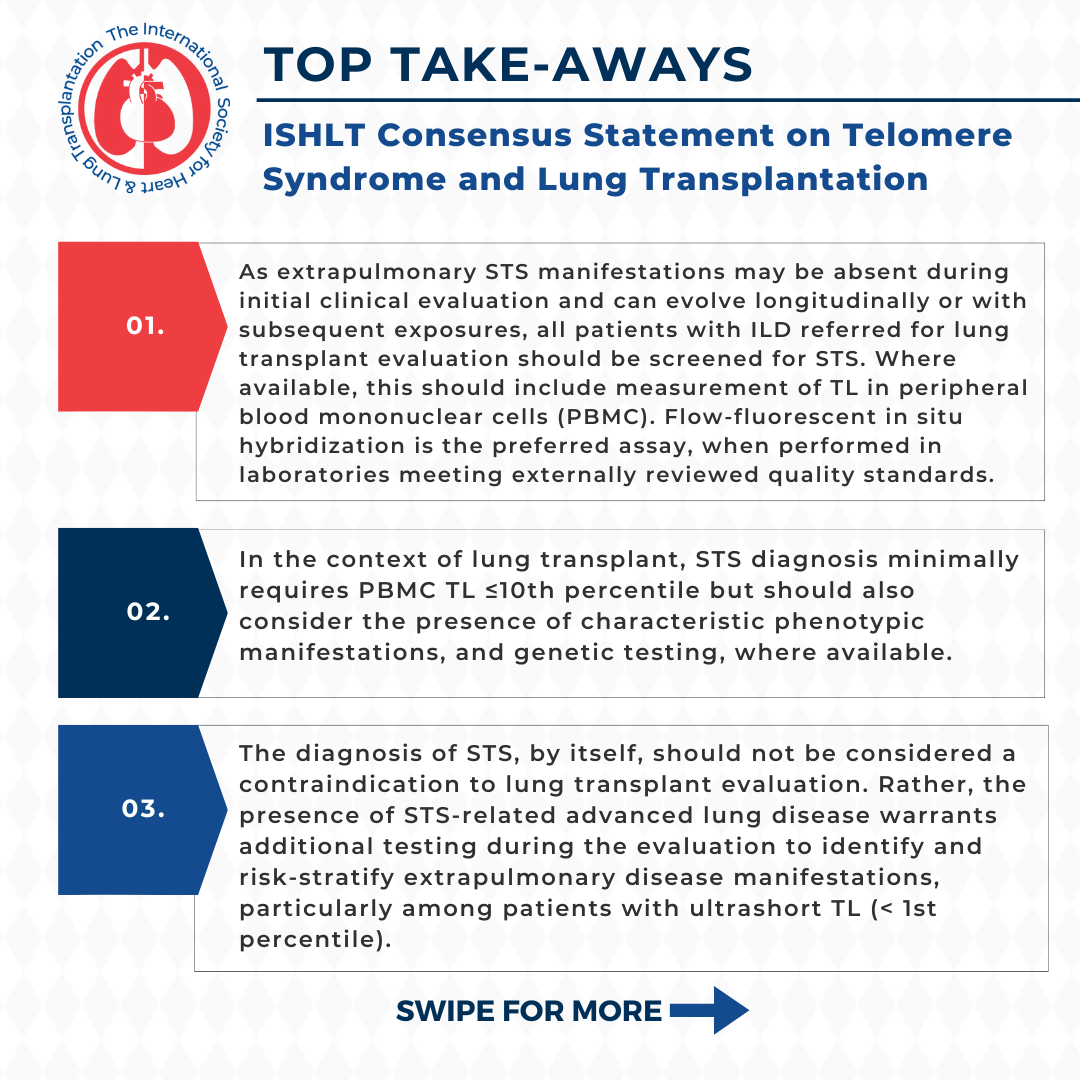
Top Takeaways
Click to view larger image and all top takeaways.
Related Guidlines
-
EPPVDN Expert Consensus Statement on the Diagnosis and Treatment of Paediatric Pulmonary Hypertension
-
Donor Heart and Lung Procurement: A Consensus Statement
-
ISHLT Statement on Vaccines in Transplant Recipients
-
Consensus Statements from the ISHLT Consensus Conference: Heart Failure Related Cardiogenic Shock
-
ISHLT Consensus Statement for the Standardization of Bronchoalveolar Lavage in Lung Transplantation

