Considerations for Endpoints in Lung Transplant Clinical Trials: An ISHLT Consensus Statement
Published 16 December 2025
John Greenland, MD, PhD; Michael Perch, MD; Kieran Halloran, MD, MSc; Deborah Levine, MD; Eric Morrell, MD, MA; Anna Reed, MBChB; Ciara Shaver, MD, PhD; Jonathan Singer, MD, MS; Stuart Sweet, MD, PhD; Robin Vos, MD, PhD; Shambhu Aryal, MD, FCCP; Nicholas Avdimiretz, MD, FRCPC; Fay Burrows, BPharm; Daniel Calabrese, MD; Fiorella Calabrese, MD; Silvia Campos, PhD; Michael Combs, MD, MS; Marc de Perrot, MD, MSc, FRCSC; Göran Dellgren, MD, PhD; Joshua Diamond, MD, MS; Thomas Egan, MD, MSc; Patricia Ging, MSc; David Glidden, PhD; Martin Goddard, MB BCh, FRCS, FRCPath; Soma Jyothula, MD; Michael Keller, MD; Hrishikesh Kulkarni, MD, MSCI; Johanna Kwakkel-van Erp, MD, PhD; Vibha Lama, MD, MS; Nandor Marczin, MD, PhD; Tereza Martinu, MD, MHS; Megan Neely, PhD; Scott Palmer, MD, MHS; Caroline Patterson, BMBS, MD; Elizabeth N. Pavlisko, MD; Christine Pham, PharmD; Melissa Sanchez, PsyD, MSc; Hans Henrik Schultz, MD, PhD; Nicolaus Schwerk, MD, PhD; Unmil Shah, MD; Michael Shashaty, MD, MSCE; Lianne Singer, MD; Patrick Smith, PhD, MPH; Laurie Snyder, MD, MHS; Melinda Solomon, MD, MSc; Stijn Verleden, PhD; Veronique Verplancke, MD; Adriana Zeevi, PhD, ABHI; Jamie Todd, MD, MHS
J Heart Lung Transplant. December 2025.
Clinical Trials are the cornerstone of an evidence-based approach to improve lung transplant outcomes. However, barriers to clinical trials in this field include a lack of clarity as to the value of specific clinical trial endpoints, the time needed to reach some endpoints, and the complexities in how trials should be structured given the heterogeneity and small size of the lung transplantation population.
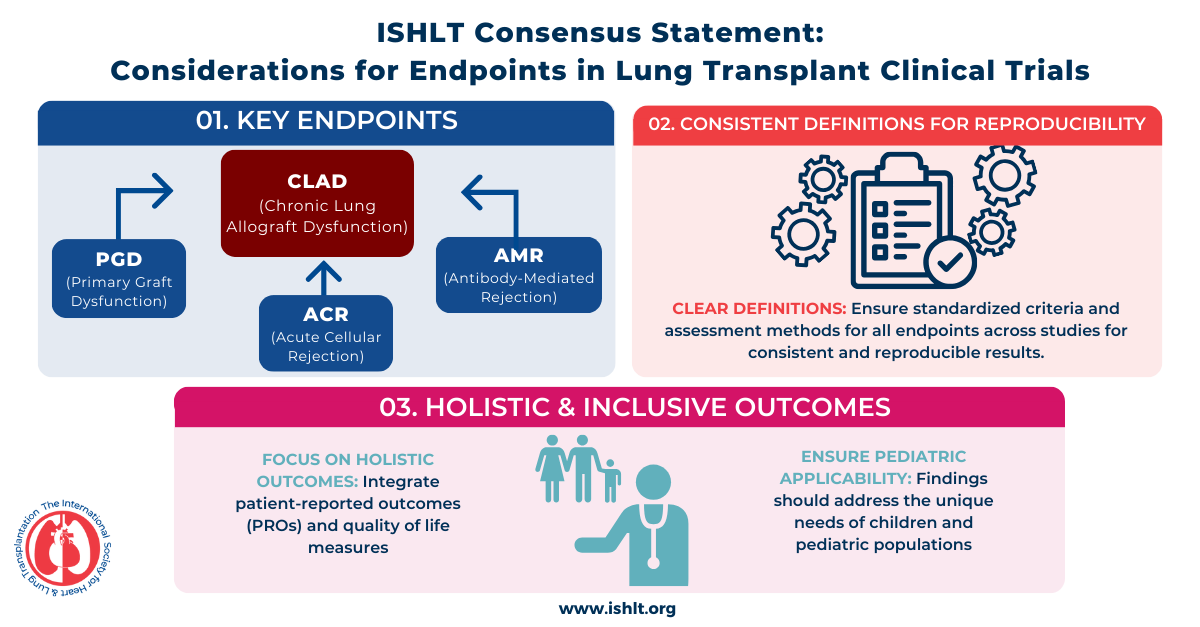
To address this challenge, a multidisciplinary working group of 49 experts from ISHLT developed this consensus statement to present expert opinions on the considerations and definitions for endpoints, which may be targeted in clinical trials of novel interventions aimed at improving lung recipient outcomes. For each included endpoint, the document describes the relationship of the endpoint to mortality or other clinically meaningful longer-term outcomes and gives recommendations on the approach to measure, operationalize, and, if applicable, adjudicate these conditions when used as trial endpoints.
This document provides practical guidance for operationalizing these endpoints and outlines their optimal use in clinical trials. By standardizing trial design, these recommendations aim to accelerate the development of urgently needed therapies to improve lung transplant outcomes.
Read the Perspective Piece at JHLT Download the Perspective Piece
The ISHLT Perspective Piece is a new document type developed to accompany all ISHLT Documents and is specifically designed for print publication in JHLT. The piece The piece will set the context for the document in an easy-to-read manner and serves as an opportunity for writing groups to speak directly to the heart and lung transplant community about the rationale behind each document, its most important takeaways, and the hard work that went into creating it.
Top Takeaways
Click to view larger image and all top takeaways.
Related Guidlines
-
ISHLT Statement on Vaccines in Transplant Recipients
-
Consensus Statements from the ISHLT Consensus Conference: Heart Failure Related Cardiogenic Shock
-
2020 ACC/AHA Clinical Performance and Quality Measures for Adults With Heart Failure
-
Donor Heart and Lung Procurement: A Consensus Statement
-
Present Status of Research on Psychosocial Outcomes in Cardiothoracic Transplantation— Review and Recommendations for the Field

